Understanding and improving product or service quality is crucial for any business that wants to remain competitive. To achieve consistent quality, professionals rely on a set of tried and tested techniques known as quality control tools. These tools help identify problems, analyze processes, and implement improvements that enhance overall efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What Are Quality Control Tools?
Quality control tools are systematic techniques and methods used to monitor, assess, and improve quality within processes. Originally popularized in Japanese manufacturing, these tools have now become standard across various industries worldwide. Using these tools allows teams to pinpoint defects, eliminate inefficiencies, and maintain quality standards at every stage of production or service delivery.
In modern industries, quality professionals frequently utilize Quality Control Tools to visually analyze data and track down the root causes of recurring issues. These tools not only help in troubleshooting but also in making informed decisions based on evidence, which ultimately leads to more stable and efficient processes.
Importance of Using Quality Control Tools
Implementing Quality Control Tools provides organizations with the ability to maintain consistency, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction. By addressing issues early through data-driven analysis, companies can prevent larger problems down the line. These tools are especially beneficial for quality assurance teams aiming to meet compliance standards and achieve continuous improvement.
From manufacturing to healthcare, Quality Control Tools have proven to be effective in ensuring that each step of the workflow meets predefined standards. This enables organizations to deliver reliable and high-quality outputs with minimal variations.
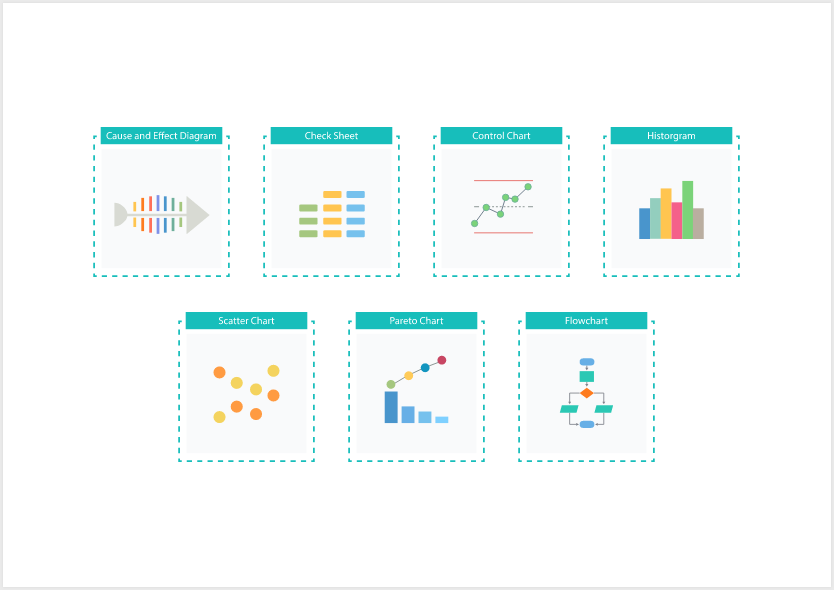
The 7 Basic Quality Control Tools
These seven tools are often referred to as the “Seven Basic Tools of Quality” and are foundational to any quality management system:
- Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram)
Helps identify potential causes of problems and categorize them for deeper analysis. - Check Sheet
A simple document used to collect real-time data at the location where the data is generated. - Control Charts
Monitor process variation over time and help detect trends or abnormalities. - Histogram
Provides a visual representation of data distribution to identify patterns. - Pareto Chart
Highlights the most significant factors contributing to a problem based on the 80/20 rule. - Scatter Diagram
Shows the relationship between two variables and helps detect correlations. - Flow Chart (Process Diagram)
Illustrates the step-by-step process, making it easier to identify inefficiencies or redundancies.
How to Implement These Tools Effectively
To get the most from these tools, it’s essential to first train relevant staff on how to use and interpret each tool correctly. Start by identifying a specific quality issue, select the most appropriate tool for analysis, and use real data for insights. Collaboration between departments is also critical to ensure accurate data collection and effective action planning.
Conclusion
Quality Control Tools are indispensable for any business focused on continuous improvement and long-term success. By incorporating these tools into regular workflows, organizations can proactively manage quality, reduce costs, and ensure customer satisfaction. Whether you’re just beginning your quality journey or refining a mature system, mastering these tools is a valuable investment.