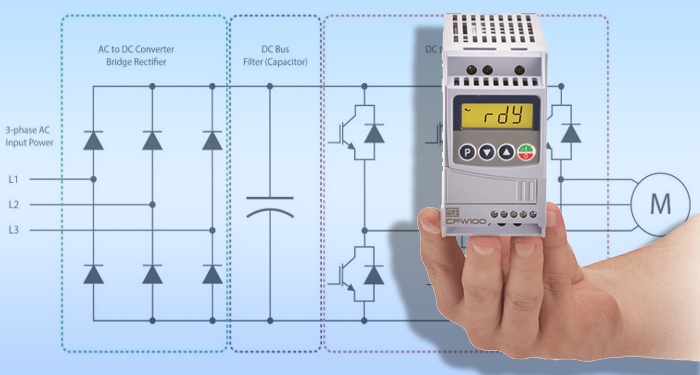
Industrial automation relies on precise motor control to enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve productivity. DC Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) play a critical role in achieving these goals by adjusting motor speed, torque, and power consumption based on real-time demands. This article explores the significance of DC VFDs in industrial automation, their benefits, and common applications.
1. What is a DC Variable Frequency Drive?
A DC Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is an electronic device that regulates the speed and power of a DC motor by controlling the voltage and frequency supplied to it. Unlike fixed-speed motors, which operate at a constant speed, DC VFDs allow dynamic speed control, making them ideal for industrial automation systems that require precision and adaptability.
2. Key Benefits of DC VFDs in Industrial Automation
a. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
- Adjusts motor speed based on demand, reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
- Minimizes power wastage, leading to lower electricity costs in manufacturing plants.
- Some advanced VFDs feature regenerative braking, which converts excess kinetic energy into usable electrical power.
b. Improved Process Control
- Enables real-time speed adjustments, ensuring seamless operation in assembly lines, conveyor systems, and robotic applications.
- Provides precise torque control, reducing mechanical stress and enhancing product quality.
c. Extended Equipment Lifespan
- Soft start and stop functionality reduces motor wear and tear by gradually ramping up or down power.
- Protects motors from voltage spikes, overload conditions, and excessive heat, increasing durability.
d. Enhanced Automation and Remote Monitoring
- Integrates with PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems for centralized control.
- Supports remote monitoring, allowing operators to adjust parameters without manual intervention.
e. Reduced Maintenance Costs
- Prevents mechanical failures by optimizing motor performance.
- Eliminates frequent replacements of mechanical components, lowering downtime.
3. Industrial Applications of DC VFDs
a. Conveyor Systems
- Controls belt speed based on load variations, improving material handling efficiency.
- Reduces mechanical stress, extending conveyor motor life.
b. Robotics and Automated Machinery
- Provides precision movement control for robotic arms and CNC machines.
- Enhances repeatability and accuracy in automated manufacturing.
c. Pumps and Fans
- Regulates the speed of water pumps and ventilation fans in industrial plants.
- Minimizes energy use by adjusting motor speed to real-time demand.
d. Cranes and Hoists
- Ensures smooth lifting and lowering of heavy loads with precise torque control.
- Prevents sudden jerks, improving operational safety.
e. Packaging and Material Handling
- Improves automated sorting, cutting, and assembly processes.
- Synchronizes motor speed with conveyor systems for seamless packaging operations.
f. Renewable Energy Systems
- Controls DC motors in solar panel tracking systems and wind turbines.
- Enhances power generation efficiency by optimizing motor output.
4. Conclusion
DC Variable Frequency Drives are indispensable in modern industrial automation, offering energy efficiency, precision control, and reduced maintenance costs. By integrating DC VFDs, industries can enhance productivity, improve system reliability, and reduce operational expenses. As automation technology advances, the role of DC VFDs will continue to expand, making them a vital component in the future of smart manufacturing.